Configure Jenkins using Nginx Reverse Proxy on Ubuntu 22.04 on AWS
A quick guide to configure jenkins using Nginx Reverse Proxy on Ubuntu 22.04 on AWS
Introduction:
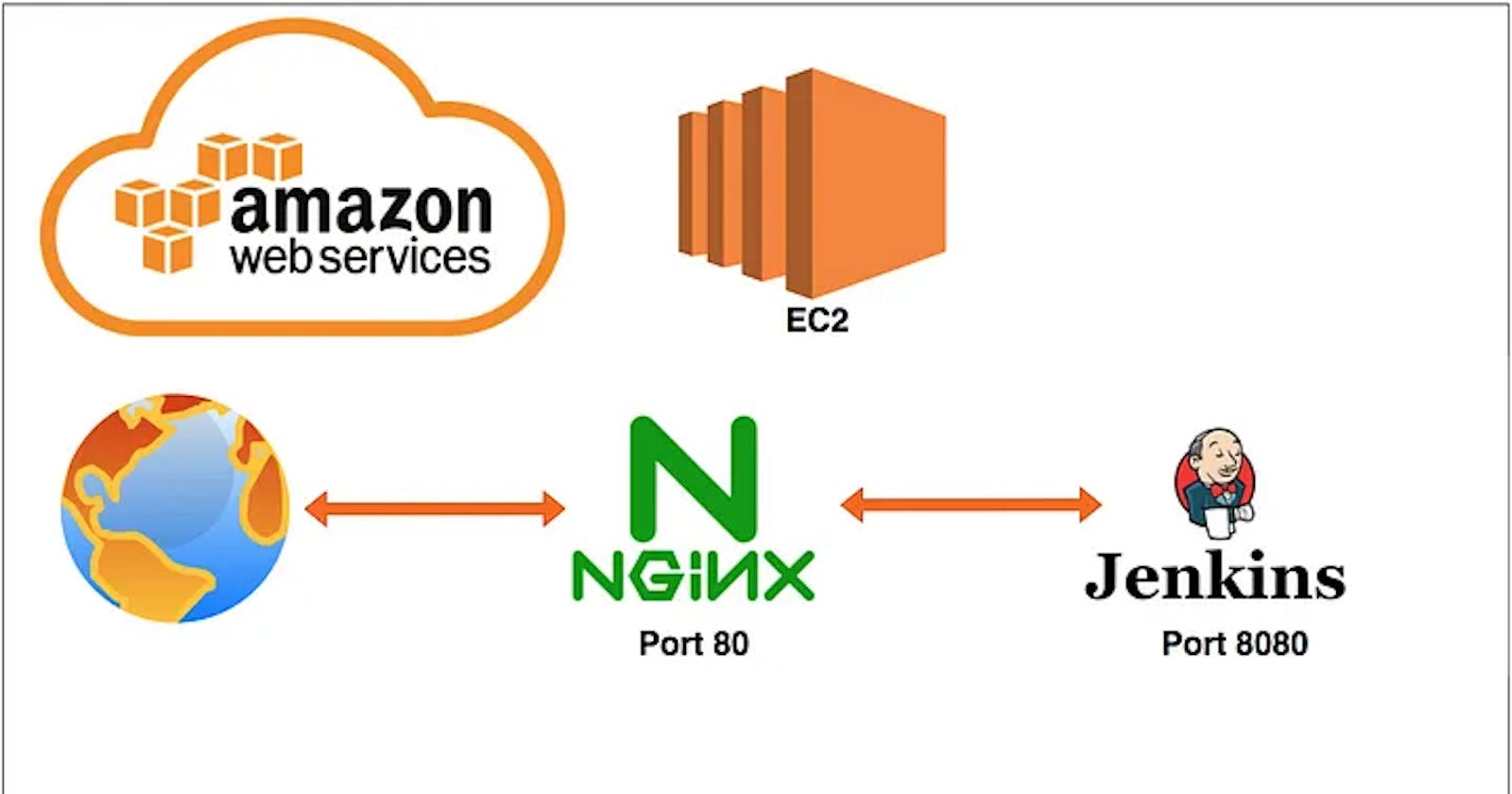
In this post, we will be installing Jenkins on an EC2 instance running Ubuntu, and configuring a reverse proxy using Nginx. I have used the t3.small instance and hosted my domain on Route 53.
Jenkins is a popular open-source automation server used for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. By installing Jenkins on an EC2 instance, we can leverage the scalability and flexibility of AWS to automate our development and deployment processes.
Configuring a reverse proxy using Nginx is a common way to improve security and performance when serving web applications
Install Jenkins:
Update Package Repository and Upgrade Packages:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgradeInstall Adoptium Java 17, Add Adoptium Repository
wget -O - <https://packages.adoptium.net/artifactory/api/gpg/key/public> | tee /etc/apt/keyrings/adoptium.asc echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/adoptium.asc] <https://packages.adoptium.net/artifactory/deb> $(awk -F= '/^VERSION_CODENAME/{print$2}' /etc/os-release) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/adoptium.listUpdate the Repo and Add Java 17
apt update apt install temurin-17-jdk /usr/bin/java --version exitNow it's time to install Jenkins. First, add the repository key to the system:
curl -fsSL <https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key> | sudo tee \\ /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \\ <https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable> binary/ | sudo tee \\ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkinsIt's time to start Jenkins.
sudo systemctl start jenkinsTo ensure that Jenkins is running properly, it is important to verify that it has started successfully. As systemctl does not display status output, we need to rely on the status command to check the status of Jenkins. By using the status command, we can confirm that Jenkins has started and is running without any issues.
sudo systemctl status jenkinsIf everything is working correctly, the status output at the beginning will indicate that the service is currently active and set to start automatically during boot.

Access Jenkins User Interface
To set up your installation, access Jenkins on its default port, 8080, by using your server's domain name or IP address: http://your_server_ip_or_domain:8080
Install Nginx Reverse Proxy for Jenkins:
Nginx is a highly popular and widely used web server that can host some of the biggest and most visited sites on the internet. It is a lightweight option that can function as either a web server or reverse proxy. Due to its versatility, it provides a great deal of flexibility to its users. Nginx is designed to efficiently handle a large number of concurrent connections, which makes it an excellent choice for high-traffic websites. It is well-known for its high performance, stability, and scalability. Nginx can be easily configured and customized according to the user's needs.
📌 Prerequisites: Jenkins server already installed and running
Update Package Repository and Upgrade Packages
sudo apt update sudo apt upgradeInstalling Nginx
sudo apt install nginxChecking Your Web Server
To confirm that the service is running, type the following command using the
systemdinit system:systemctl status nginxWe can check with the systemd init system to make sure the service is running by typing:

Check your Web Server is running
http://your_server_ipWe need to see this output:

Configuring as Reverse proxy - Nginx Go to the directory
/etc/nginx/conf.dand create a file named jenkins.conf, And paste the following content:upstream jenkins { keepalive 32; # keepalive connections server 127.0.0.1:8080; # jenkins ip and port } # Required for Jenkins websocket agents map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade { default upgrade; '' close; } server { listen 80; # Listen on port 80 for IPv4 requests server_name jenkins.nishanthgowda.xyz; # replace this with your server domain name # this is the jenkins web root directory # (mentioned in the output of "systemctl cat jenkins") root /var/cache/jenkins/war/; access_log /var/log/nginx/jenkins.access.log; error_log /var/log/nginx/jenkins.error.log; # pass through headers from Jenkins that Nginx considers invalid ignore_invalid_headers off; location ~ "^/static/[0-9a-fA-F]{8}\\/(.*)$" { # rewrite all static files into requests to the root # E.g /static/12345678/css/something.css will become /css/something.css rewrite "^/static/[0-9a-fA-F]{8}\\/(.*)" /$1 last; } location /userContent { # have nginx handle all the static requests to userContent folder # note : This is the $JENKINS_HOME dir root /var/lib/jenkins/; if (!-f $request_filename){ # this file does not exist, might be a directory or a /**view** url rewrite (.*) /$1 last; break; } sendfile on; } location / { sendfile off; proxy_pass <http://jenkins>; proxy_redirect default; proxy_http_version 1.1; # Required for Jenkins websocket agents proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; proxy_max_temp_file_size 0; #this is the maximum upload size client_max_body_size 10m; client_body_buffer_size 128k; proxy_connect_timeout 90; proxy_send_timeout 90; proxy_read_timeout 90; proxy_buffering off; proxy_request_buffering off; # Required for HTTP CLI commands proxy_set_header Connection ""; # Clear for keepalive } }Next, check for syntax errors in your Nginx files to ensure they are error-free. Run the following command.
sudo nginx -tYou should get a similiar output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulNow, to ensure that the changes made to the nginx configuration file are reflected, we need to restart the nginx service:
sudo systemctl restart nginxNow, you can see Jenkins up and running through the NGINX server.

Under Manage Jenkins, we can get the below error in some cases.

To fix this error, you can go to the "Configure System" section under "Manage Jenkins". In this section, find the "Jenkins Location" setting and update the URL to match your custom URL. This should resolve the error and allow Jenkins to be accessed using your custom URL.

Now that you've configured Nginx to act as a reverse proxy for Jenkins, you should be able to access Jenkins by navigating to your domain name. Simply enter your domain name into your web browser's address bar and hit enter to test this. If everything has been set up correctly, you should be able to access Jenkins from your domain name without any issues.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, we have successfully installed Jenkins on an EC2 instance running Ubuntu, and configured a reverse proxy using Nginx. By hosting our domain on Route 53, we were able to easily manage DNS records and route traffic to our EC2 instance. With these tools in place, we have created a robust and scalable infrastructure for our Jenkins deployment.
Jenkins is a powerful automation server that can help streamline our development and deployment processes. By using AWS, we can take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing to create a reliable and secure Jenkins deployment.
I hope that this tutorial has helped guide you through the process of installing Jenkins and configuring Nginx as a reverse proxy. With this knowledge, you can now create a powerful CI/CD pipeline that can help automate your development and deployment workflows.